You're reading the documentation of the v1.0. For the latest released version, please have a look at v1.1.
Generic Interferometer
GenericInterferometer usage example
It is possible to define a generic interferometer with the class
perceval.components.GenericInterferometer.
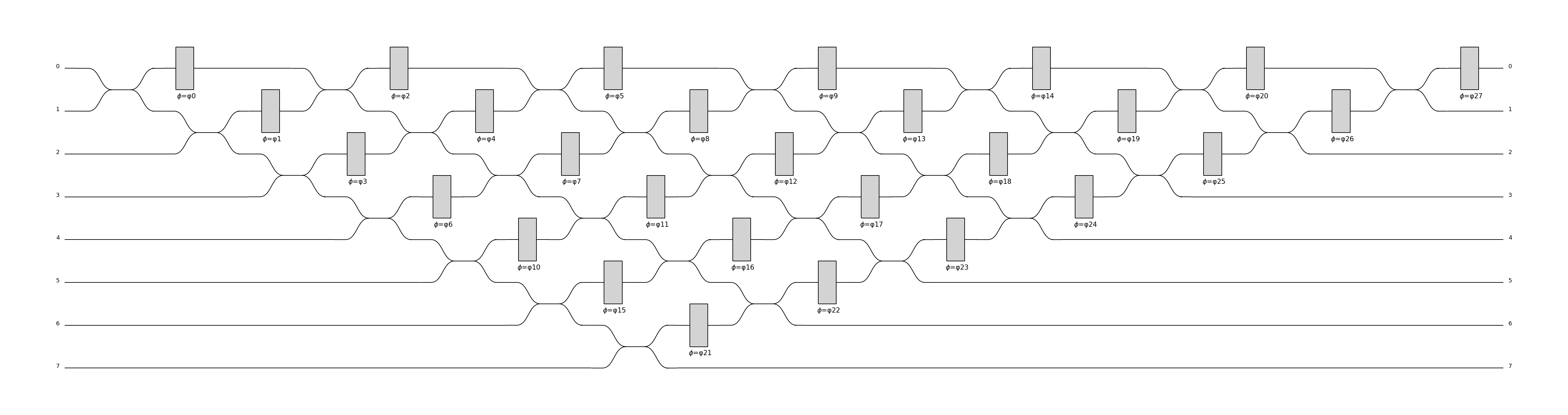
For instance, the following defines a triangular interferometer on 8 modes using a beam splitter and a phase shifter as base components:
>>> c = pcvl.GenericInterferometer(8,
... lambda i: comp.BS() // comp.PS(pcvl.P("φ%d" % i)),
... shape=pcvl.InterferometerShape.TRIANGLE)
>>> pcvl.pdisplay(c)
GenericInterferometer code reference
- enum perceval.utils._enums.InterferometerShape(value)
An enumeration.
Valid values are as follows:
- RECTANGLE = <InterferometerShape.RECTANGLE: 0>
Rectangular matrix of universal 2-modes components (e.g. MZI). All paths have the same depth.
- TRIANGLE = <InterferometerShape.TRIANGLE: 1>
Triangular mesh of universal 2-modes components. The top of the interferometer has max depth, the bottom mode has depth 1.
- class perceval.components.generic_interferometer.GenericInterferometer(m, fun_gen, shape=InterferometerShape.RECTANGLE, depth=None, phase_shifter_fun_gen=None, phase_at_output=False, upper_component_gen=None, lower_component_gen=None, align_with_barriers=True)
Generate a generic interferometer circuit with generic elements and optional phase_shifter layer
- Parameters:
m (
int) – number of modesfun_gen (
Callable[[int],ACircuit]) – generator function for the building components, index is an integer allowing to generate named parameters - for instance:fun_gen=lambda idx: pcvl.BS()//(0, pcvl.PS(pcvl.P(f"phi_{idx}")))shape (
InterferometerShape) – The output interferometer shape (InterferometerShape.RECTANGLE or InterferometerShape.TRIANGLE)depth (
Optional[int]) – if None, maximal depth is \(m-1\) for rectangular shape, \(m\) for triangular shape. Can be used with \(2*m\) to reproduce [25].phase_shifter_fun_gen (
Optional[Callable[[int],ACircuit]]) – a function generating a phase_shifter circuit.phase_at_output (
bool) – if True creates a layer of phase shifters at the output of the generated interferometer else creates it in the input (default: False)upper_component_gen (
Optional[Callable[[int],ACircuit]]) – generator function for the building the upper component, index is an integer allowing to generate named parameters - for instance:upper_component_gen=lambda idx: pcvl.PS(pcvl.P(f"phi_upper_{idx}"))lower_component_gen (
Optional[Callable[[int],ACircuit]]) – generator function for the building the lower component, index is an integer allowing to generate named parameters - for instance:lower_component_gen=lambda idx: pcvl.PS(pcvl.P(f"phi_lower_{idx}"))
- property mzi_depths: list[int]
Return a list of MZI depth, per mode
- remove_phase_layer()
Remove the optional phase layer at the input or at the output. Does nothing if such a layer does not exist
- set_identity_mode()
Set the interferometer in identity mode (i.e. photons are output on the mode they’re input)
- set_param_list(param_list, top_left_pos, m)
Insert parameters value starting from a given position in the interferometer.
This method is designed to work on rectangular interferometers
- Parameters:
param_list (
list[float]) – List of numerical values for the parameterstop_left_pos (
tuple[int,int]) – Starting position of the insertion (column#, row#). Position is handled MZI-wise (i.e. (0,0) starts inserting values on the top-left-most MZI of the interferometer whereas (1,0) starts on top of the 2nd MZI column). The optional phase layer is ignored in the position handling.m (
int) – Mode count on where to insert the parameter values