You're reading the documentation of the v1.0. For the latest released version, please have a look at v1.1.
Analyzer
The Analyzer algorithm aims at testing a processor, computing a probability table between input states and expected
outputs, a performance score and an error rate.
For example, we call the Naive backend that we store in simulator_backend:
>>> simulator_backend = pcvl.BackendFactory().get_backend('Naive')
We can create an input state that will enter our optical scheme later on. We store it in input_state and use BasicState from the Perceval library.
>>> input_state = pcvl.BasicState("|1,1>")
let’s simulate the distribution obtained when we input two photons in a beam-splitter. We will use the Naive backend already stored in simulator_backend.
We will simulate the behavior of the circuit using the Circuit Analyzer which has three arguments:
The first one is an instance of a processor containing the circuit to analyse.
The second one is the input state (we will use input_state).
The third one is the desired output states. To compute all possible output states, one just input “*”.
>>> p = Processor("SLOS", comp.BS()) # create a processor running on SLOS backend
>>> ca = pcvl.algorithm.Analyzer(p, [input_state], "*")
Then, we display the result of Analyzer via pdisplay.
>>> pcvl.pdisplay(ca)
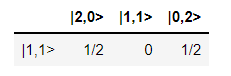
- class perceval.algorithm.analyzer.Analyzer(processor, input_states, output_states=None, mapping=None, **kwargs)
Analyses a set of input states vs output states probabilities.
- Parameters:
processor (
AProcessor) – the processor to analyseinput_states (
list[BasicState] |dict[BasicState,str]) – list of BasicStates or a mapping {BasicState: name}output_states – list of output states. Valid values are: * None (then, the input states are taken as output states) * a list of BasicState * a mapping {BasicState: name} * the string “*” meaning oll possible target states are generated
mapping – optional mapping {BasicState: name} used for display
kwargs – as the Analyzer internally uses a Sampler instance, it needs a “max_shots_per_call” value
- col(output_state)
Return the column number for a given output state in the distribution matrix
- Parameters:
output_state (
BasicState) – any computed output state- Return type:
Optional[int]- Returns:
the column number, or None if the output state is unknown
- compute(normalize=False, expected=None, progress_callback=None)
Iterate through the input states, generate (post-selected) output states and calculate distance with expected, if provided.
- Parameters:
normalize (
bool) – whether to normalize the output statesexpected (
Optional[dict]) – optional mapping between states in ideal caseprogress_callback – optional callback to inform the user of the task progress